

Risk Management
We identify, analyze, and assess various risks surrounding our business based on future projections and changes in the internal and external environment, and implement measures to avoid, mitigate, transfer, or acknowledge, etc., related to these risks. In addition, by monitoring the situation, we promote risk management in accordance with the following principles with the goal of appropriately managing risks and supporting the management of the Group.
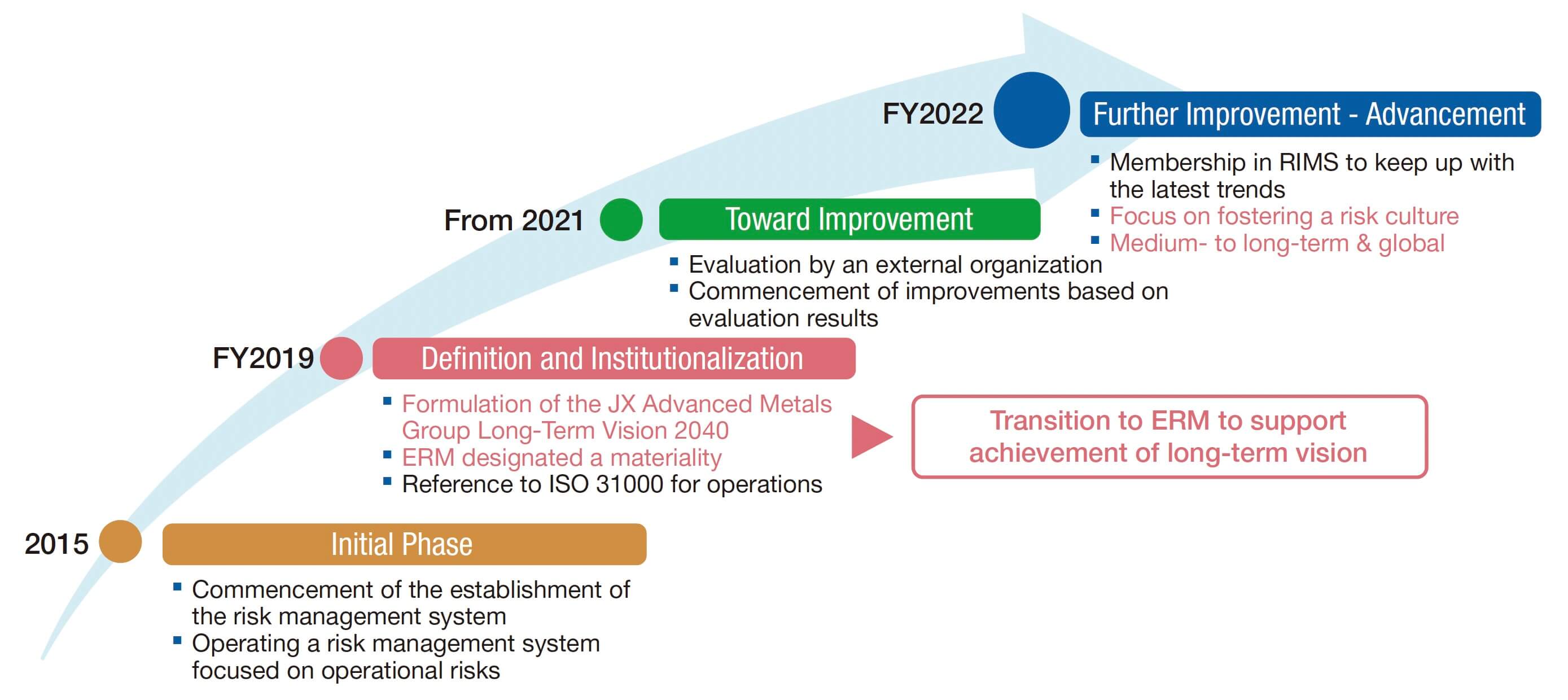
The Progress and Future Vision of ERM
- Involve all management personnel and employees
- Recognize risks linked to business goals and promote them as an organization-wide activity
- Review risks and risk response plans, taking into account the organization’s purpose, mission, and goals, as well as internal and external conditions
- Continuously improve based on evaluation of the effectiveness of our initiatives and feedback from stakeholders
Risk Management Advancement and Promotion System
The JX Advanced Metals Group regards enterprise risk management (ERM*) as an essential element in achieving our long-term vision. We are committed to continuous improvement to enhance the effectiveness of our ERM practices.
We first established our risk management system in 2015 and focused on operational risks. In 2019, the formulation of Long-Term Vision 2040 prompted the transition to a risk management approach that supports the achievement of this vision. We shifted from traditional risk management activities to the implementation of ERM, referencing ISO 31000. We then worked to strengthen risk management capabilities to enhance corporate value in preparation for our listing on the Tokyo Stock Exchange, and continue to aim for alignment of ERM with management strategy.
- *A system or process to ensure that risk management is implemented in an organized, systematic, effective, and continuous manner in order to increase the certainty of achieving the organization’s objectives and goals.
Enterprise Risk Management Governance Structure
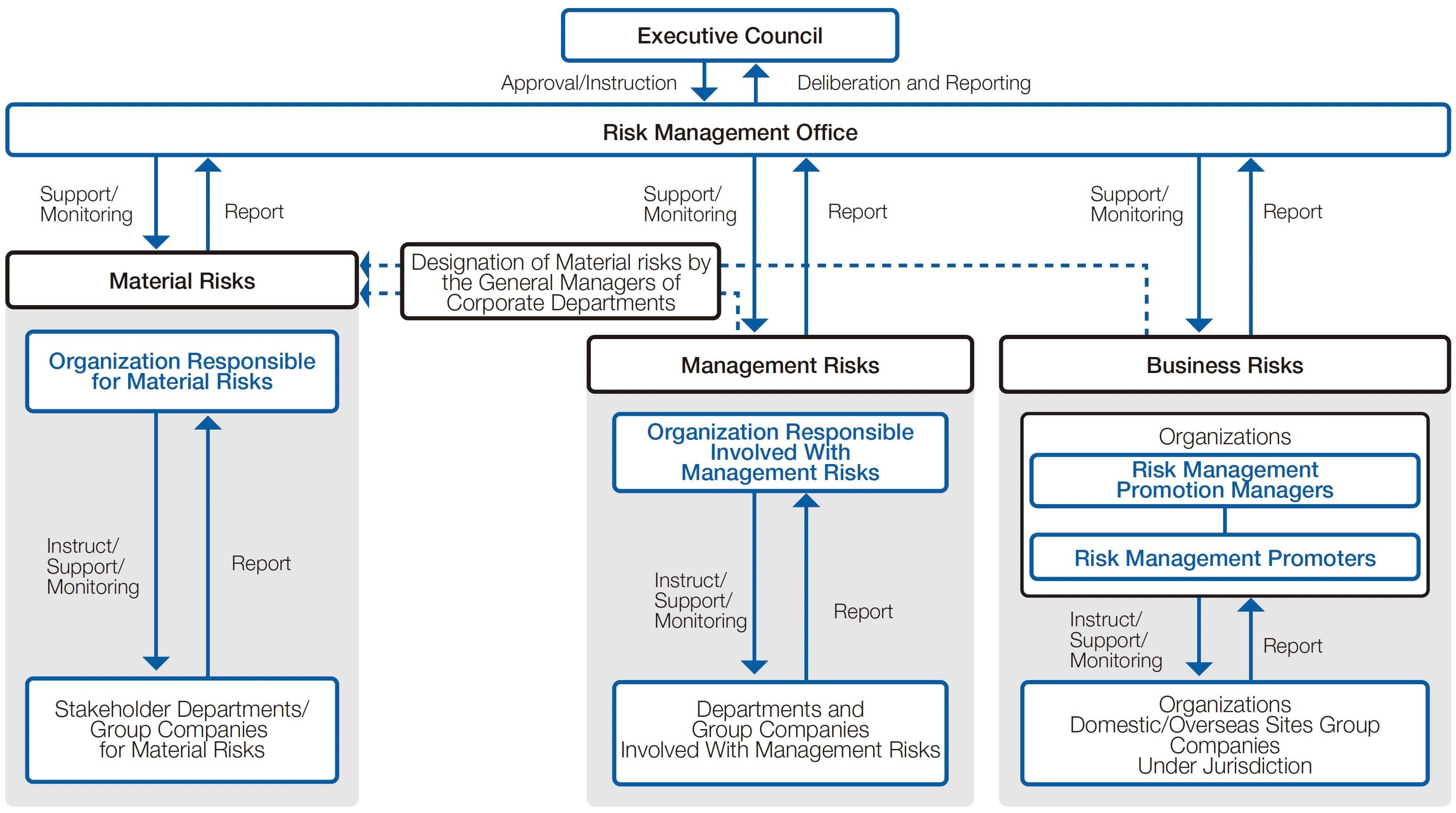
Under the ERM framework, the JX Advanced Metals Group determines material risks, approves response plans for each material risk, and monitors these plans, at the JX Advanced Metals Executive Council. In addition, the Risk Management Office is responsible for the overall risk management for both the Company and the Group, and implements ERM.
Risk Definition and Classification
Risk is defined as “any and all uncertainty that could have an impact on the management of JX Advanced Metals Group companies.” Here, to achieve risk management that is linked to our long-term vision, medium-term management plan, and business plan, we classify risks into management risks and business risks. Among management risks and business risks, risks that we determine will have a significant impact on the Group’s management, and that should be addressed on a company-wide basis, are designated as material risks by the Executive Council. Material risks include risks related to technology, business continuity, and geopolitical risks. The department responsible for these material risks takes the lead in implementing risk responses. In addition, the Executive Council monitors the status of these actions.
- 1.Management Risks
Risk of obstructing achievement of the management goals of the JX Advanced Metals Group. These risks are selected by consensus from the general managers of corporate departments. - 2.Business Risks
Risks that may affect the achievement of goals related to the execution of business by the respective organization. The organizations responsible for each risk select business risks through a business risk identification survey. Each organization appoints risk management promotion managers and risk management promoters, with the goal of embedding risk management activities within each organization. - 3.Material Risks
Management and business risks that are selected by the Executive Council as risks that could have a significant impact on the management of the JX Advanced Metals Group. The Executive Council approves and monitors risk response.
Business Risks
We conduct an annual business risk identification survey when formulating our management plan. This survey requires the organizations responsible for each risk (including subordinate organizations, business sites, and group companies under supervisory divisions), to identify, analyze, and evaluate risks that may hinder the achievement of business targets. Risks assessed as higher in priority (ranked based on impact and likelihood of occurrence) are reported to the respective risk supervisory divisions, which consolidate the results for submission to the Risk Management Office. The responsible organizations, acting as risk owners, mitigate or transfer identified risks throughout the year, and take appropriate risk response measures. To confirm risk status, we conduct semiannual monitoring to track changes, review progress, and evaluate the effectiveness of countermeasures.
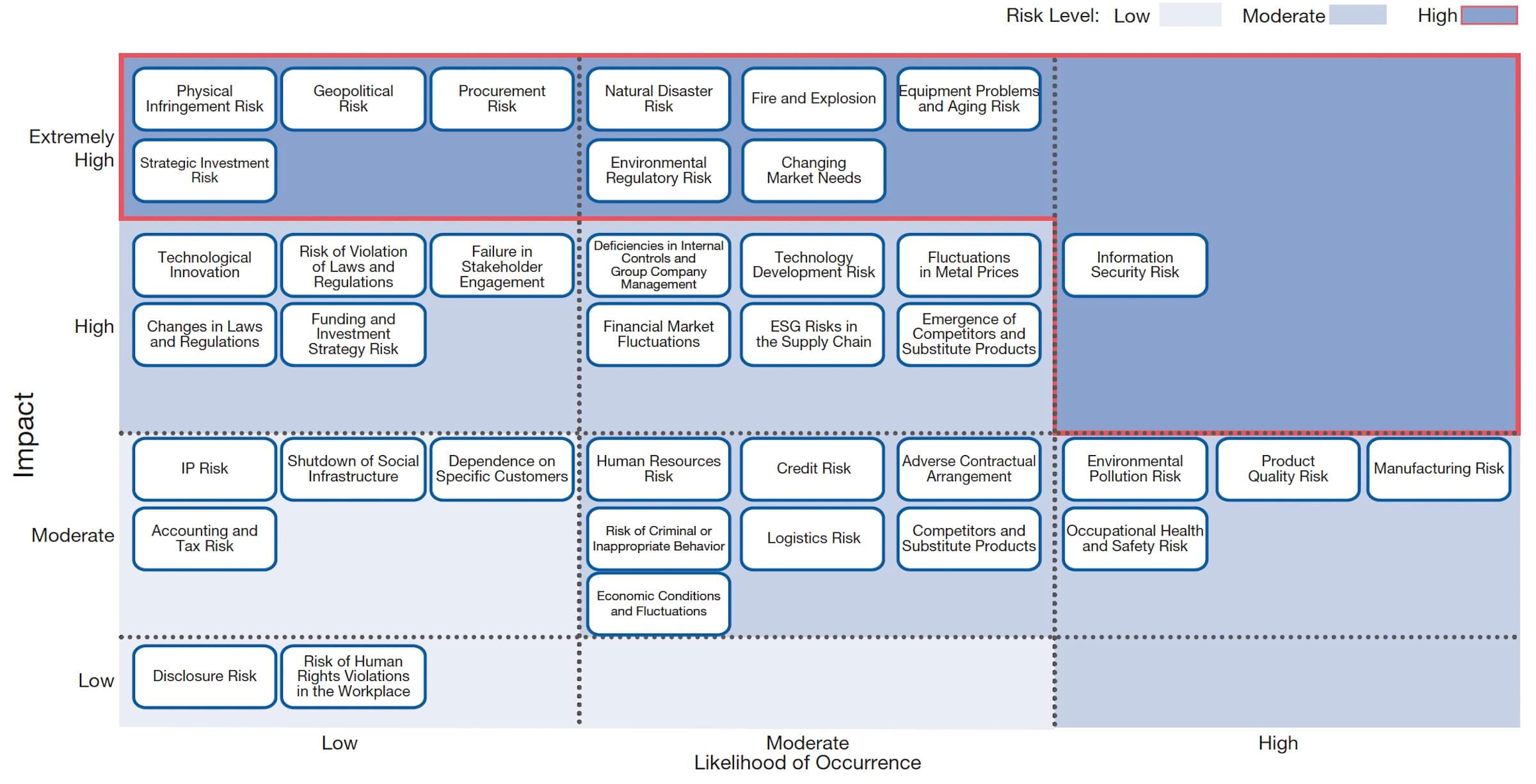
We analyze reported risks across 45 categories based on impact and likelihood of occurrence, and report the results to management in the form of a risk map (heat map). This process visualizes material risks, clarifies priorities, and provides management with risk information that supports effective decision-making.
Through this framework, we advance risk management aligned with our management strategy, support the achievement of business targets, and ensure accountability to stakeholders.
Heat Map
Material Risks
We begin identifying and addressing material risks when formulating medium-term management plans. The process involves the participation of key members of the Group’s management, such as the general managers of corporate and business divisions, as well as the president and vice presidents. This ensures that management’s perception of a risk is correctly reflected as a material risk.
Identified Material Risks and Risk Awareness * Refer to 2. Business Conditions, (3) Business and Other Risks in the Annual Securities Report for more details (Japanese Only).
| Risk Category | Risk Awareness and Mitigation Initiatives |
|---|---|
|
Risk of Losing Competitive Advantage in Focus Businesses |
Our Focus Businesses include the Semiconductor Materials and ICT Materials segments. These segments secure competitive advantage by building strong relationships of trust with customers, which enable us to quickly grasp and respond appropriately to customer needs and the latest development trends. Efforts to maintain this advantage include advancing research and development, securing intellectual property rights for advanced technologies and preventing third-party infringement, strengthening supply chain resilience, enhancing quality control systems, and expanding production capacity. However, we may lose this competitive advantage if our responses fail to meet customer needs or if changes in the business environment, including the emergence of substitute products or shifts in demand, persist. |
|
Geopolitical Risk |
The Group operates business sites worldwide through an established global network. The Mineral Resources Business invests in, explores, and develops copper and minor metal mines, including the Caserones mine in Chile. Our Metals & Recycling and Tantalum and Niobium Businesses procure raw materials internationally and pursue stable sourcing of essential raw materials for semiconductor and information and communications materials. We collaborate with the think tanks within the Group to gather information from open sources and other channels and provide this information quickly across the organization. Geopolitical risks surrounding mineral resources are increasing, leading to concerns about raw material procurement. Such risks include resource nationalism, conflict minerals, and restrictions on recycled raw materials. Intensifying international political conflicts could disrupt the supply chain for our products and affect business continuity. Overseas Group operations also face potential exposure to litigation, disputes, or other legal proceedings. We monitor the issues and progress of these cases on a regular basis and judge that they do not pose a material threat to business continuity. However, significant settlement payments or damages from multiple lawsuits could affect Group business results and financial position. |
|
Natural Disaster Risk |
Natural disasters have grown more severe in recent years due to abnormal weather patterns. The Group operates numerous business sites in Japan and overseas, and large-scale natural disasters, including earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, or heavy snowfall, could disrupt supply chains and damage assets. Such disruptions or damage may lead to delays or suspension of supply to customers, deterioration in earnings, and threats to human life. To prepare against such incidents, the Group established a business continuity plan based on our crisis and emergency response regulations. We conduct regular training and ongoing improvements to minimize human and material damage and enable early recovery. However, natural disasters that exceed our expectations could impair business continuity. |
|
Sustainability Risk |
Stakeholders in recent years increasingly call for broader sustainability initiatives to achieve a decarbonized and recycling-oriented society, conserve biodiversity and water resources, and respect human rights. The Group positions achieving a sustainable society as a priority issue in our management policy under the long-term vision. To this end, we identified six materialities for priority action and actively implement initiatives in line with these materialities. However, inadequate future response to stricter stakeholder expectations or tighter national regulations could lead to the termination of business relationships or contraction of operations. Such outcomes could significantly affect Group business results and financial position. |
|
Human Resources Risk |
Recruiting and retaining talent has become more challenging amid the declining labor force in Japan, resulting from an aging and shrinking population, and the diversification of work values among younger generations. The Group works to recruit and retain skilled talent by fostering an organizational culture able to adapt to change. Our efforts include revising personnel systems, enabling flexible job transfers, and building frameworks that allow diverse employees to thrive. However, inadequate response to future labor market changes could result in higher turnover and difficulties in hiring, leading to prolonged labor shortages. These conditions may disrupt business operations and significantly affect Group business results and financial position. |
Execution and Enhancement of Risk Transfer Strategies
Our approach to risk is to select and implement an appropriate response (transfer, mitigation, retention, or avoidance) to the relevant risk based on the results of risk assessment. For risks that could pose a serious impact on our business operations despite risk reduction measures, we utilize insurance as a means of risk transfer. We are working with relevant departments to optimize insurance on a global basis by reviewing the results of our surveys on insurance policies held by the Group in Japan and overseas and enhancing the effectiveness of insurance for the Group.
Toward Advanced of ERM
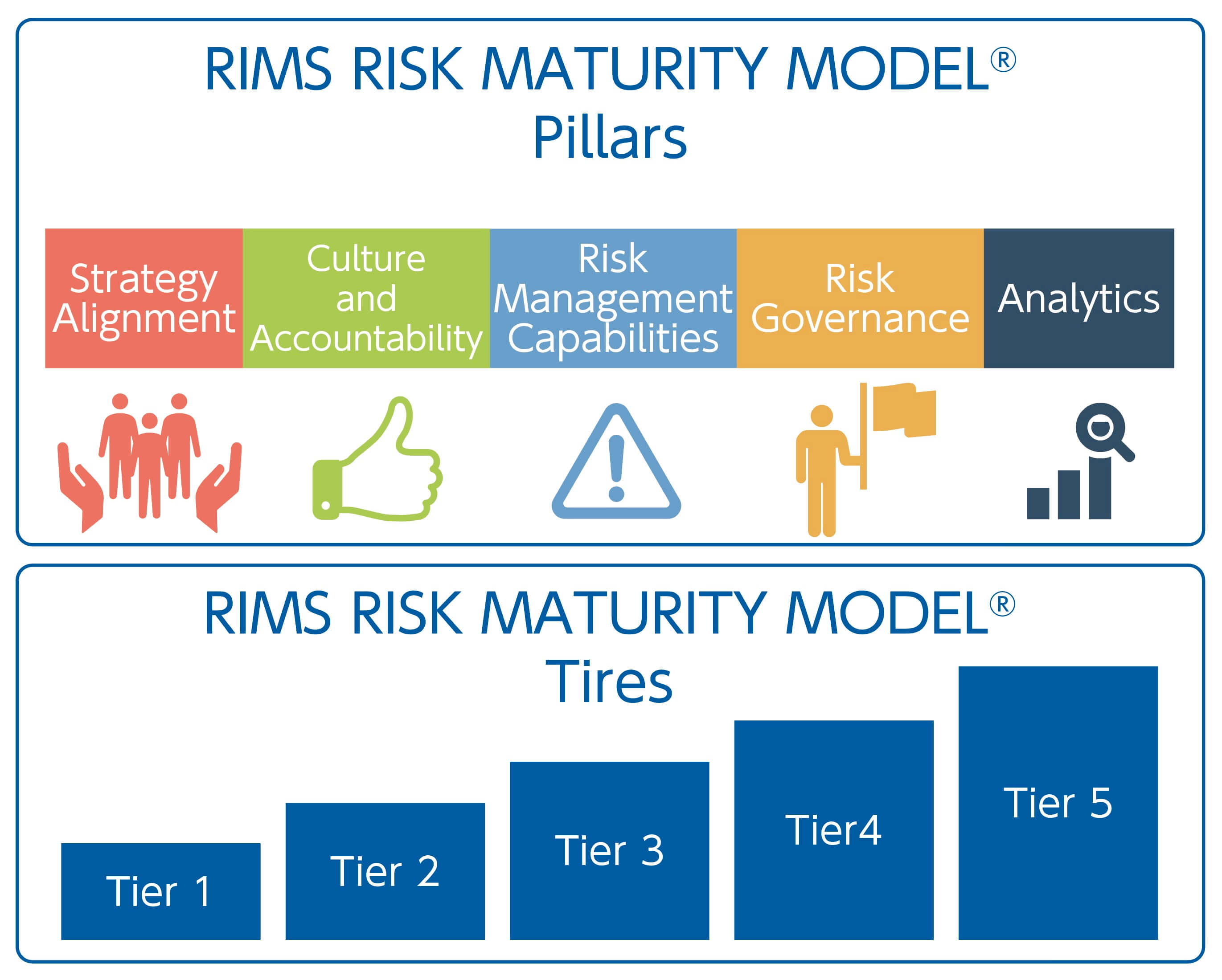
In advancing ERM, we utilize the Risk Management Society's ("RIMS*") maturity model. This model defines the status for each pillar, such as Strategy Alignment, at various tiers. These are compared to the Group’s ERM status to assess maturity.
After setting the desired goals, we regularly conduct a gap analysis between the defined state at each tier and the current state of our group's ERM. This helps us identify the challenges we face in reaching the next tier. By implementing measures to resolve these challenges, we can achieve more effective ERM.
- *Based in New York, this is the world's largest risk management organization, with more than 9,000 risk management professionals as members worldwide.
Risk Management Activity Framework
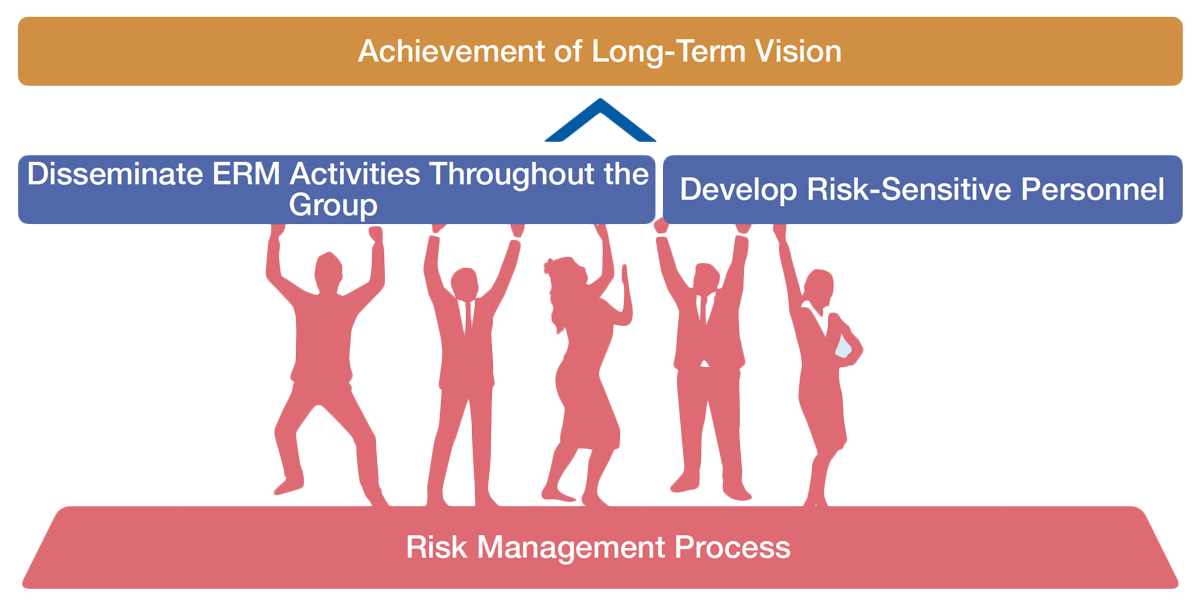
Based on the results of the maturity assessment, we have identified the dissemination of ERM activities throughout the Group and the development of risk-sensitive personnel as the two key elements to promote for achieving a more effective ERM. Specifically, through our outreach efforts, we aim to deepen under-standing among all officers and other employees in our group regarding the importance of ERM and its connection to our management strategy by consistently highlighting these points. Additionally, through personnel development, we aim for individuals at various levels and roles to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for effective risk management.
We incorporate and implement these elements into actual activities by ensuring risk management functions as a company-wide initiative. To this end, we develop processes and strengthen collaboration with the organizations responsible for each risk. The organizations responsible for each risk and the Risk Management Office communicate with each other through reviews and interviews conducted during various initiatives, including the business risk identification survey and monitoring activities. These bodies collaborate to refine risk information and develop effective countermeasures.
Ultimately, the goal is for employees at all levels in each organization within the Group to fulfill the risk management roles required by their positions and to operate the ERM system autonomously.
Disseminate ERM Activities Throughout the Group
Regular awareness-raising to enhance each individual's daily risk management practices
We regularly publish Risk Management Newsletter, an in-house newsletter dedicated to risk management, with the aim of making risk management accessible to each employee and promoting its dissemination throughout the Group. For example, we feature articles such as, "What does the president consider risk management?" in which we interview the president. There are also articles regarding the latest trends in global risk, as well as those featuring good examples of how risk is handled within the Group.
Risks are not limited to Japan, but exist everywhere in any business organization, regardless of its size or location. To this end, in fiscal 2023, we also began publishing an English version of the newsletter to promote risk management among employees in all regions.
We conduct reader surveys twice a year to continuously monitor the level of dissemination, and we develop our initiatives based on the feedback received from these surveys.

Acquiring Skills to Enhance Each Individual’s Daily Risk Management Practices
(1) Target-Specific Training
Based on the Risk Management Training System, we are implementing training tailored to specific target groups in a phased manner. In each organization responsible for risks, e-learning and comprehension tests are conducted at the time of appointment for those in charge of risk management promotion. This ensures that they are equipped to lead the annual business risk assessment and risk response, allowing them to exercise their abilities as leaders in their respective organizations.
The program provides an overview of the Group's risk management activities and explains to newly appointed managers, leaders, chiefs, and newly graduated employees the expected roles for each position. The Risk Management Office also holds in-house cross-organizational study groups on an annual basis, where we deliver lectures on the fundamentals of risk management to all employees.
| Target Group | Objective |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| All employees (including those covered above) | Fostering Risk Sensitivity |
(2) Member Skill Set
The Risk Management Office is committed to improving the competence of our members. Specifically, we have established our own skill sets of the skills and knowledge required to perform risk management tasks, and visualize the status of acquisition of these skills for our office members. Each member conducts a self-assessment during the performance evaluation period and, through discussions with their supervisor, works on improving their individual capabilities.
In the future, we will establish and develop skill sets not only for Risk Management Office members, but also for risk management promotion managers and promoters assigned to each business division, group company, and plant in an effort to broadly support the development of risk management talent.
| Knowledge and Skills Required for Members of the Risk Management Office |
Classification | Outputs (Outputs That Can Be Expected From Having the Knowledge and Skills) | Output Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Understanding Business Operations | Knowledge |
|
Level 1-3 |
| Key Business Processes of the Risk Management Office | Knowledge |
|
Level 1-3 |
| Knowledge of Contract Formation | Knowledge |
|
Level 1-3 |
| Knowledge of Insurance | Knowledge |
|
Level 1-3 |
Risk Management Process
Identifying Risks and Conducting Scenario Planning in Collaboration With Management After Trend Analysis
Within the Group, we are working to implement risk management linked to our long-term vision, medium-term plan, and business plan by establishing three categories of risk: business risks, management risks, and material risks.
Process for Initiating Risk Response for Material Risks
Material risks will be identified and risk responses initiated in conjunction with the timing of the medium-term management plan, according to the following steps. The process involves the participation of key members of the Group’s management, such as the general managers of corporate and business divisions, as well as the president and vice presidents. This ensures that management’s perception of a risk is correctly reflected as a material risk.
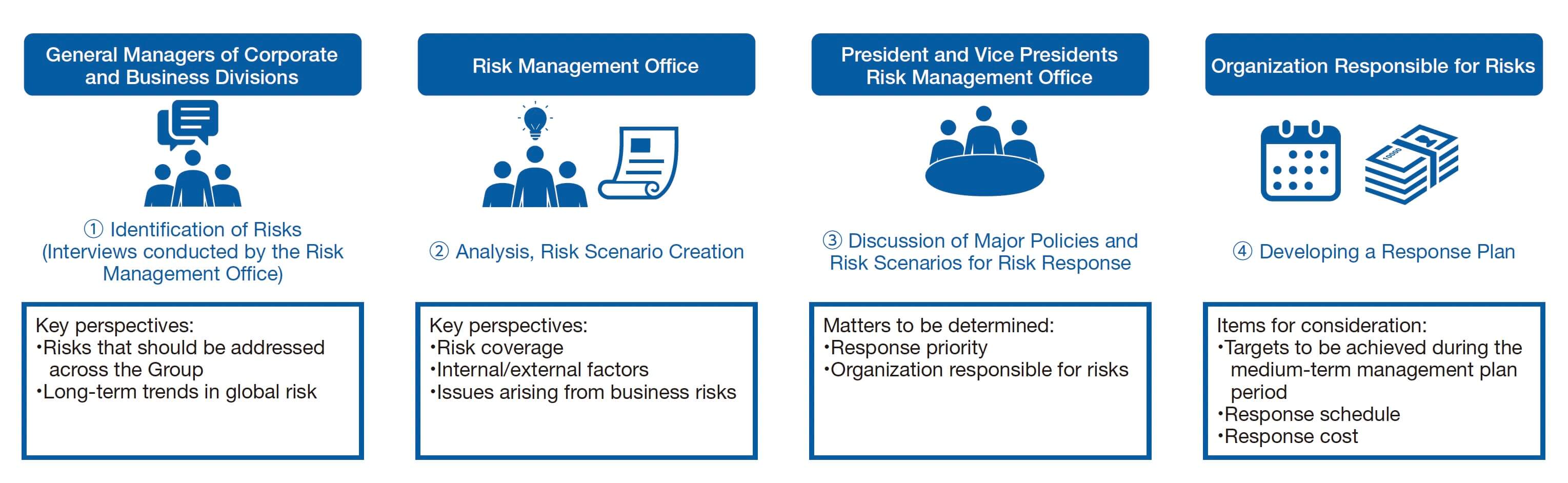
Importance of Scenario Planning
Risk scenarios are developed for all material risks. Risk scenarios are documented descriptions that outline the causes of risks manifesting and the potential effects on the Group if these risks were to materialize. The benefits of developing risk scenarios are as follows.
(1) Risk response includes activities to prevent risks before they occur and activities to minimize the impact if they do occur. The more clearly we define causes in risk scenarios, the easier it is to identify the most appropriate actions to take.
(2) By verbalizing risks and their impacts in detail as risk scenarios, we can correctly identify risks and ensure a unified recognition of these risks by all members of the Group, especially management. All risk scenarios will be finalized through discussions between the president and vice presidents.
Risk scenarios should not be created once and left unchanged; they need to be revised in response to changes in the internal and external environment. Instead of thinking about revising scenarios after change occurs, we are focused on using our imaginations to prepare for what if scenarios, and striving to embed this mindset within the organization.
Business Continuity Plan Initiatives
The Group has formulated business continuity plans (BCP) to minimize damage and achieve early recovery in the event of business interruption due to a major earthquake.
From fiscal 2020, we have taken this to a higher level and have begun working toward the establishment of an all-hazard BCP called a resource-based BCP.
This is not a BCP for individual events, such as earthquakes or floods, but one that focuses on resource contingencies (facilities, raw materials, materials, etc.) that are likely to disrupt business activities during emergencies, and organizes relevant disaster mitigation and recovery measures.
We also conduct regular assessments of disaster risks at major business sites, including those overseas. This information aids in making decisions related to preventive measures and capital investments to mitigate potential damages. Through these initiatives, we aim to strengthen our BCP.
We continue efforts to improve initial response through efficient and reliable means of information sharing in the event of a natural disaster.
In fiscal 2024, we conducted joint training exercises across our head office, Hitachi Works, Isohara Works, and Kurami Works. The exercises served as initial emergency response drills assuming damage to the head office and covered (1) establishing and operating an emergency response headquarters at alternate offices and plants , (2) confirming the safety of personnel, (3) assessing internal and external damage to the company, and (4) sharing this information and handing over the emergency response headquarters back to the head office after recovery. The scenarios for these drills were kept confidential in advance. Moving forward, we will continue to enhance the effectiveness of our BCP through regular training sessions, as we work on establishing business continuity management.
Information Security Initiatives
Information Security Initiatives
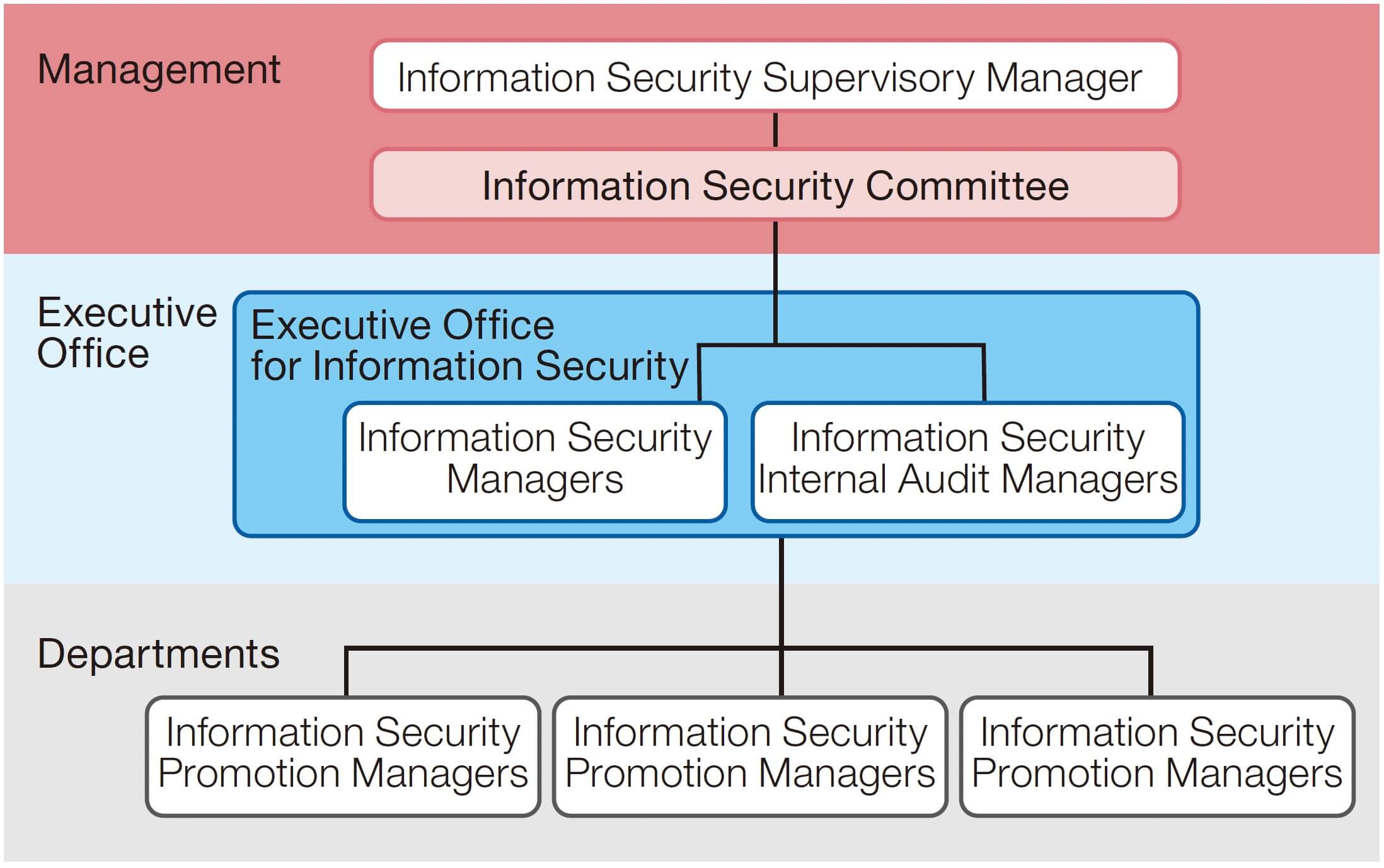
The Group has taken steps to build an information security management system (ISMS) in compliance with ISO 27001 from the three perspectives of strengthening information security compliance, increasing customer trust, and leveraging information internally and externally.
In fiscal 2024, we conducted information security risk assessments, internal audits, rank-based training, and supplier management in each department in accordance with plans approved by the Information Security Supervisory Manager. To solidify information security measures and awareness within the Group, we are extending their application to Group companies, in addition to the head office and business sites.
In efforts to upgrade information security further under the leadership of the Information Security Supervisory Manager, we will incorporate the cyber security measures implemented by the IT Department. At the same time, we pursue continuous improvement in accordance with ISMS to contribute to the realization of our long-term vision of becoming a technology-based company.
JX Advanced Metals Group Basic Policy Concerning Information Security
We, the JX Advanced Metals Group, recognize that the information assets that support our products and technology are critical assets. In order to strive to maintain our advantage in business competition, we will systematically and continuously engage to strengthen information security in accordance with the following policy.
- 1.We will comply with laws and regulations, the guidelines set forth by the national government, and the obligations under contracts, etc. related to information security.
- 2.We will strive to ensure reliable protection of information assets entrusted to us by our customers and business partners.
- 3.We will implement appropriate management of information assets, which are the source of the JX Advanced Metals Group’s competitiveness.
- 4.We will prevent the occurrence of information security incidents. Should an incident occur, we will minimize the impact of the incident and develop and implement measures to prevent recurrence.
- 5.We will establish an information security management system, carry out continual improvements and train human resources through information security education.
- Established on 1 November 2020
Revised on 1 November 2025
