Copper Titanium Alloy
Prototype*NKT322(HC)
- *Checking the ability for mass production.
For Technical data, S-S curve data and other data not listed, please contact us via the inquiry form.
NKT322(HC)
High conductive Copper Titanium Alloy (UNS Alloy No. C19910)
Overview
We have further enhanced the electrical conductivity by optimizing the manufacturing conditions with same chemical composition as the conventional NKT322.
Features
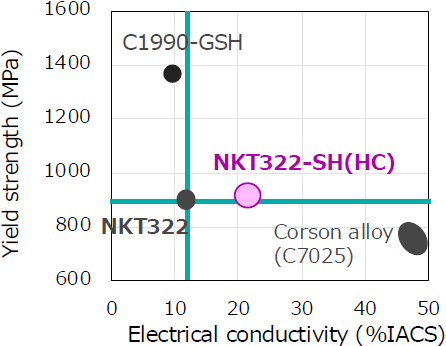
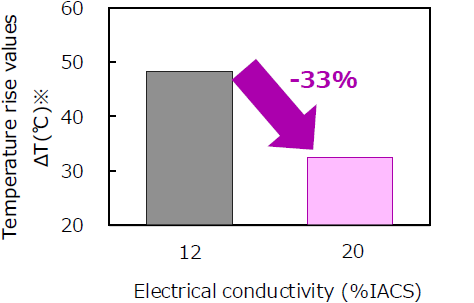
- Compared to the conventional NKT322, the electrical conductivity has improved by approximately 70%, contributing to increased current capacity and reduced heat generation in electronic components.
- It has the same strength and fatigue property as the conventional NKT322.
Table 1. NKT322(HC) chemical composition (%)
| Cu | Ti | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard composition | Remainder | 3.2 | 0.2 |
Table 2. Physical properties of NKT322(HC)
| Electrical conductivity | 20 | %IACS (@20℃) |
|---|---|---|
| Specific resistivity | 86 | nΩ·m (@20℃) |
| Thermal conductivity | 89 | W/mK |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 18.0 | ×10-6/K (20 to 300℃) |
| Modulus of elasticity | 120 | GPa |
| Specific gravity | 8.70 |
Table 3. Mechanical properties of NKT322(HC) (upper: typical values, lower: specification range)
| Temper | Tensile strength (MPa) |
Yield strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Vickers hardness (Hv) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | 1020 - |
915 - |
10 - |
315 - |
- Standard values are shown for tensile strength, Yield strength, and elongation, while typical values are given for Vickers hardness.
Correlation between Yield strength and Electrical conductivity
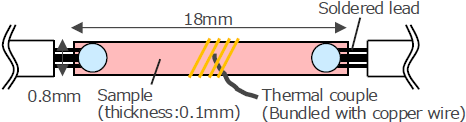
Comparison of temperature rise values
Contact Information
From the Web
Inquiries accepted 24 hours a day
