Copper Titanium Alloy ― The best alternative to beryllium copper
Compare Features and Typical Applications
Copper Titanium Alloy
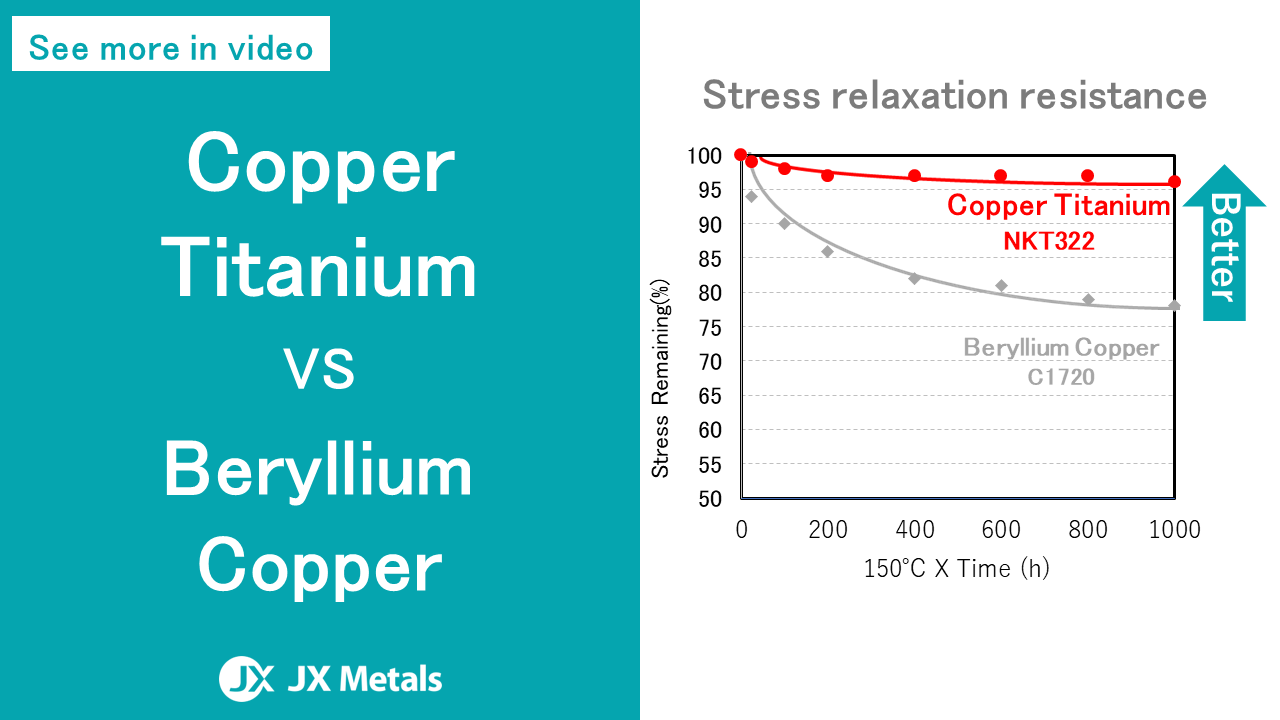
Copper Titanium is a copper alloy having titanium as the main additive element. Advantages include high strength along with excellent stress relaxation resistance and bend formability. Its properties are superior to those of beryllium copper alloy, long a representative standard for high-functionality copper alloys.
Among the main uses are for connectors and camera modules in electronic devices such as smartphones and personal computers, taking advantage of the high strength and workability. Thanks to its outstanding stress relaxation resistance, use in automotive connectors has grown in recent years.
As applications grow and the properties customers demand become more advanced as a result, we will continue our technology development toward improving properties and expanding our alloy lineup, so that such needs can be met in timely fashion.
| Alloy name | Composition | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-3Ti | Strength and bend formability superior to conventional copper titanium | Connectors, switches, jacks | |
| Cu-3Ti | Extremely High Strength at 1400MPa Higher thickness precision |
Connectors, camera modules | |
| Cu-4Ti | Copper Titanium foil having the world’s highest tensile strength of any copper alloy at 1540 MPa Higher thickness precision |
Camera Modules | |
| Cu-3.2Ti-0.2Fe | Strength (Yield strength) of 1 GPa or higher, along with excellent bend formability | Connectors, switches, jacks | |
| Cu-3.2Ti-0.2Fe | Improved strength and bend formability compared to conventional NKT322 | Connectors | |
| Cu-3.2Ti-0.2Fe | Improved conductivity with equivalent strength compared to conventional NKT322 | Connectors |
Compare Composition and Properties
Copper Titanium Alloy Composition and Properties
Chemical Composition (wt%)
| Copper Alloy Name | CuTi | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1990(HP) | C1995(HP) | NKT322 | NKT322(HB) | NKT322(HC) | |
| Chemical Composition (wt%) | Cu : Bal. Ti : 3.0 |
Cu : Bal. Ti : 4.0 |
Cu : Bal. Ti : 3.2 Fe : 0.2 |
Cu : Bal. Ti : 3.2 Fe : 0.2 |
Cu : Bal. Ti : 3.2 Fe : 0.2 |
Physical Properties
| Copper Alloy Name | CuTi | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1990(HP) | C1990-GSH(HP) | C1995-GSH(HP) | NKT322 | NKT322(HB) | NKT322(HC) | |
| Specific Gravity | 8.70 | 8.70 | 8.62 | 8.70 | 8.70 | 8.70 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | 127 | 127 | 127 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Electrical Conductivity (%IACS@20℃) | 12 | 8 | 8 | 12 | 11 | 20 |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
Mechanical Properties
| Copper Alloy Name | CuTi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1990(HP) | C1990-GSH(HP) | C1995-GSH(HP) | NKT322 | NKT322(HB) | NKT322(HC) | ||
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | H | - | - | - | 900-1000 | - | - |
| EH | 885-1080 | - | - | 920-1020 | - | - | |
| SH | 910-1110 | - | - | 970-1100 | - | (1020) | |
| ESH | 1000-1180 | - | - | 1010-1200 | 980-1200 | - | |
| XSH | - | - | - | - | 1030-1250 | - | |
| GSH | - | 1300-1600 | (1540) | - | - | - | |
| 0.2% Yield Strength (MPa) | H | - | - | - | 800-900 | - | - |
| EH | 780-930 | - | - | 850-950 | - | - | |
| SH | 810-960 | - | - | 900-1000 | - | (915) | |
| ESH | 950-1100 | - | - | 950-1050 | 950-1050 | - | |
| XSH | - | - | - | - | 1000-1100 | - | |
| GSH | - | (1390) | (1530) | - | - | - | |
| Elongation (%) | H | - | - | - | ≧12 | - | - |
| EH | ≧10 | - | - | ≧10 | - | - | |
| SH | ≧8 | - | - | ≧6 | - | (10.0) | |
| ESH | (3.0) | - | - | ≧3 | ≧2 | - | |
| XSH | - | - | - | - | ≧1 | - | |
| GSH | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Vickers Hardness (Hv) | H | - | - | - | (300) | - | - |
| EH | (300) | - | - | (310) | - | - | |
| SH | (320) | - | - | (320) | - | (315) | |
| ESH | (340) | - | - | (340) | (340) | - | |
| XSH | - | - | - | - | (350) | - | |
| GSH | - | (400) | (460) | - | - | - | |
- Standard specs. (Typical values)
Bend Formability
| Copper Alloy Name | CuTi | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1990(HP) | C1990-GSH(HP) | C1995-GSH(HP) | NKT322 | NKT322(HB) | NKT322(HC) | |||
| Minimum Bend Radius / t Badway |
H | - | - | - | 0.0 | 0.5 | - | - |
| - | - | - | t<0.15 | 0.15≦t≦0.25 | - | - | ||
| EH | 1.0 | - | - | 0.5 | 1.0 | - | - | |
| t≦0.20 | - | - | t<0.15 | 0.15≦t≦0.25 | - | - | ||
| SH | 2.0 | - | - | 1.0 | 2.0 | - | - | |
| t≦0.20 | - | - | t<0.12 | 0.12≦t≦0.22 | - | - | ||
| ESH | ≧5.0 | - | - | 2.0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | - | |
| t≦0.20 | - | - | t<0.10 | 0.10≦t≦0.20 | t=0.06 | - | ||
| XSH | - | - | - | - | - | 2.1 | - | |
| - | - | - | - | - | t=0.06 | - | ||
- Bad way 90°W-shape Bending Width=10mm
| Explanation of technical terms |
|---|
Inquiries accepted 24 hours a day